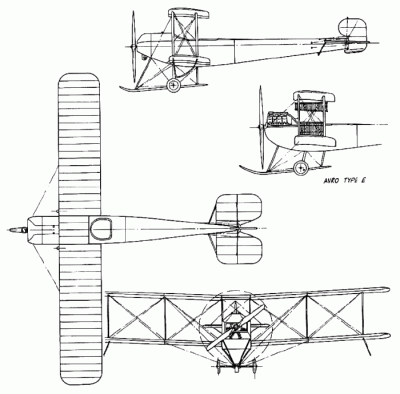
| Název: Name: | Avro 500 | Avro 500 |
| Originální název: Original Name: | Avro 500 | |
| Kategorie: Category: | cvičný letoun | trainer aeroplane |
| Výrobce: Producer: | DD.MM.1912-DD.01.1914 A. V. Roe & Co. Ltd., Manchester | |
| Období výroby: Production Period: | DD.MM.1912-DD.01.1914 | |
| Vyrobeno kusů: Number of Produced: | 18: 1 Type E prototyp / prototype 12 Type E / Avro 500 5 Type Es / Avro 502 jednomístný / one-seater | |
| První vzlet: Maiden Flight: | 03.03.1912 | |
| Osádka: Crew: | 2 | |
| Základní charakteristika: Basic Characteristics: | ||
| Vzlet a přistání: Take-off and Landing: | CTOL - konvenční vzlet a přistání | CTOL - conventional take-off and landing |
| Uspořádání křídla: Arrangement of Wing: | dvouplošník | biplane |
| Uspořádání letounu: Aircraft Concept: | klasické | conventional |
| Podvozek: Undercarriage: | pevný | fixed |
| Přistávací zařízení: Landing Gear: | kola | wheels |
| Technické údaje: Technical Data: | ||
| Hmotnost prázdného letounu: Empty Weight: | 408 1) kg | 9001) lb |
| Vzletová hmotnost: Take-off Weight: | 590 kg | 1300 lb |
| Maximální vzletová hmotnost: Maximum Take-off Weight: | ? kg | ? lb |
| Rozpětí: Wingspan: | 10.97 m | 36ft |
| Délka: Length: | 8.84 2) m | 29ft2) |
| Výška: Height: | 2.97 m | 9ft 9in |
| Plocha křídla: Wing Area: | 30.66 m2 | 330 ft2 |
| Plošné zatížení: Wing Loading: | ? kg/m2 | ? lb/ft2 |
| Pohon: Propulsion: | ||
| Kategorie: Category: | pístový | piston |
| Počet motorů: Number of Engines: | 1 | |
| Typ: Type: | Prototyp: ENV Type F o výkonu 44,7 kW Standard: Gnome Omega o výkonu 36,8 kW | Prototype: ENV Type F, power 60 hp Standard: Gnome Omega, power 50 hp |
| Objem palivových nádrží: Fuel Tank Capacity: | ? | ? |
| Výkony: Performance: | ||
| Maximální rychlost: Maximum Speed: | 99.8 km/h v 0 m | 62 mph in 0 ft |
| Cestovní rychlost: Cruise Speed: | ? km/h v ? m | ? mph in ? ft |
| Rychlost stoupání: Climb Rate: | 2.2 m/s | 440 ft/min |
| Čas výstupu na výšku: Time to Climb to: | 5 min do 610 m | 5 min to 2000 ft |
| Operační dostup: Service Ceiling: | ? m | ? ft |
| Dolet: Range: | ? km | ? mi |
| Maximální dolet: Maximum Range: | ? km | ? mi |
| Výzbroj: Armament: | - | - |
| Uživatelské státy: User States: | | |
| Poznámka: Note: | Vytrvalost: 2,5 h Prototyp: 1) 499 kg 2) 9,3 m | Endurance: 2.5 hr Prototype: 1) 1100 lb 2) 30ft 6in |
| Zdroje: Sources: | Jackson, A.J. Avro Aircraft since 1908, Putnam Aeronautical Books, London 1990. ISBN 0-85177-834-8. Goodall, M. H., Tagg, A. E. British Aricraft before the Great War. Schiffer Publishing, Atgen 2001. ISBN 0-52888-165-5. Thetford, Owen. British Naval Aircraft since 1912, Naval Institute Press, Annapolis 1991, ISBN 1-55750-076-2. Lewis, Peter. British Aircraft 1908-1914. Putnam, London 1962. http://www.airwar.ru/enc/law1/avro500.html http://www.aviastar.org/air/england/avro-500.php | |
| Period | - |
| Producer | Avro |
| Type | - |
| Camouflage | Civilní |
 Plátno / Fabric Plátno / Fabric Dřevo / Wood Dřevo / Wood Kov, stříbrná / Metalic, silver Kov, stříbrná / Metalic, silver |
|
| Country |  |
| Pilot | - |
| Production No. | - |
| Serial No. / Evidence No. | - |
| Tactical Marking / Imatriculation | - |
| Name | - |
| Unit | - |
| Base | - |
| Date (DD.MM.RRRR) | DD.MM.1912 |
| Author | - |
| Print size / 300 DPI | - |
| Published with authors permit | - |
| Author Website | - |
Prototyp Avro Type E. Na rozdíl od následujících strojů používal vidlicový osmiválec ENV
| Period | - |
| Producer | Avro |
| Type | - |
| Camouflage | Civilní |
 Plátno / Fabric Plátno / Fabric Dřevo / Wood Dřevo / Wood Kov, stříbrná / Metalic, silver Kov, stříbrná / Metalic, silver |
|
| Country |  |
| Pilot | - |
| Production No. | - |
| Serial No. / Evidence No. | - |
| Tactical Marking / Imatriculation | - |
| Name | - |
| Unit | - |
| Base | - |
| Date (DD.MM.RRRR) | DD.MM.1913 |
| Author | - |
| Print size / 300 DPI | - |
| Published with authors permit | - |
| Author Website | - |
Druhý postavený stroj, již s motorem Gnome
| Period | - |
| Producer | Avro |
| Type | - |
| Camouflage | - |
| Country | - |
| Pilot | - |
| Production No. | - |
| Serial No. / Evidence No. | - |
| Tactical Marking / Imatriculation | - |
| Name | - |
| Unit | - |
| Base | - |
| Date (DD.MM.RRRR) | DD.MM.RRRR |
| Author | - |
| Print size / 300 DPI | - |
| Published with authors permit | - |
| Author Website | - |