
Rome


Crucifixion

Development of the Roman Republican Establishment (1)

Development of the Roman Republican Establishment (2)

Development of the Roman Republican Establishment (3)

Development of the Roman Republican Establishment (4)

Development of the Roman Republican Establishment (5)

Development of the Roman Republican Establishment (6)

Development of the Roman Republican Establishment (7)

List of equipment of the Roman legionary

Pharsalus

Rewards and honors in the Roman army

Roman Camp

Roman gladiators

Saint Martin or It Started with Mars
Mars, Martin, Saint Martin What do these three have in common, or the journey from God, the protector of the harvest, through the god of the warrior to the Christian saint, the patron saint of soldiers.
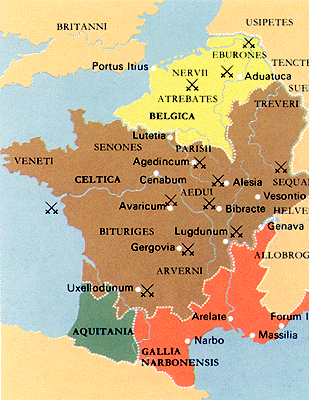
Siege of Alesia
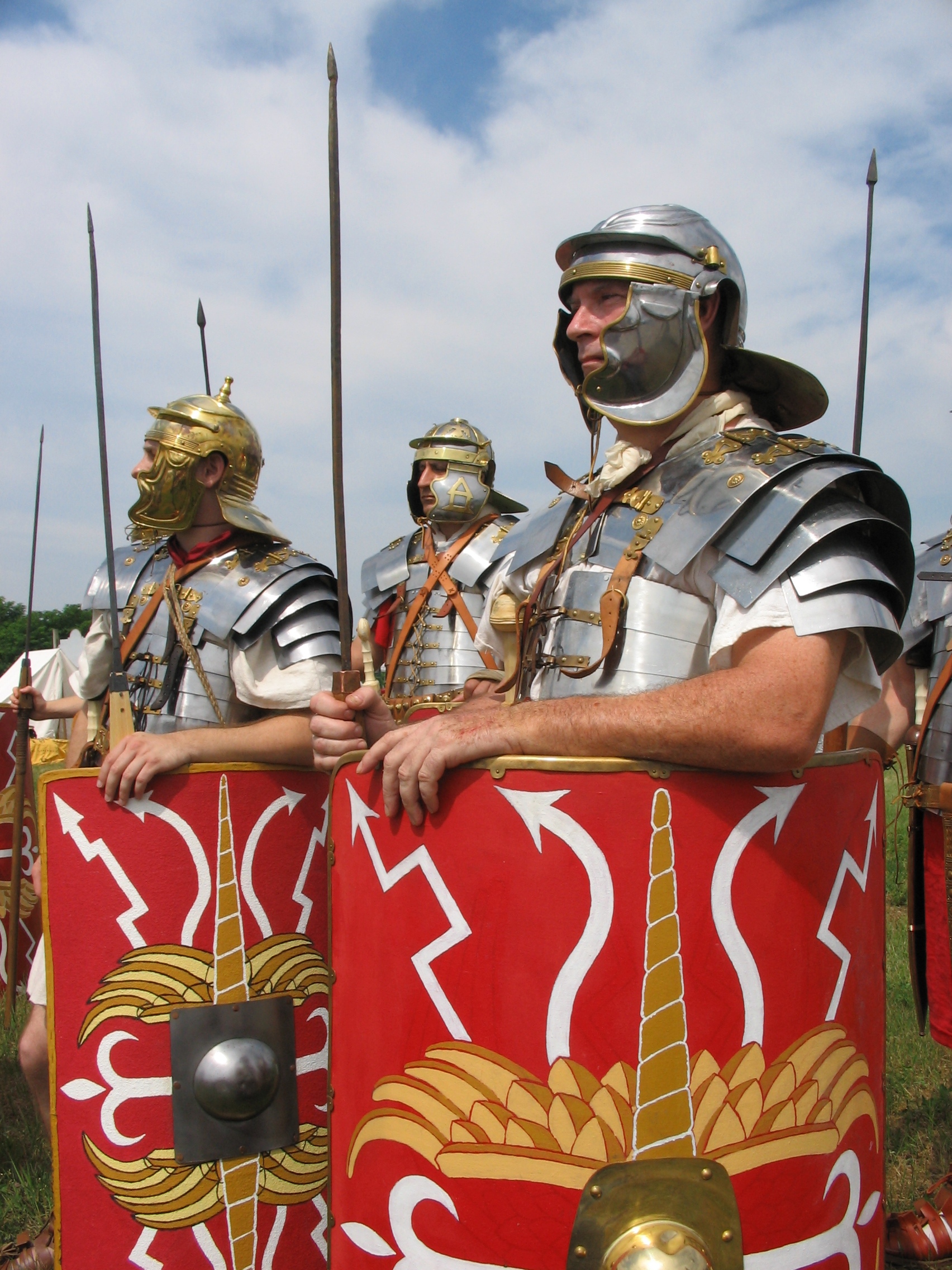

The allied corps in the Roman army

The Roman calendar as the basis of today's calendar
In this article I will discuss the Roman calendar in relation to the calendar of today. The aim is not to give an exhaustive description of the Roman calendar, but to try to explain the origins of some things that we take so much for granted that we hardly think about them - for example, why the year begins on the first of January, why the months are called what they are called in many of the world's languages, why February has 28 days, why July and August have 31 days, even though they are right after each other in the calendar, why a leap day is added to February once every four years...

Wars with Pyrrhos [281-272BC]
Pyrrhos Warin 281 BC accepted the request of the Greek city of Taranto for help in the conflict with Rome. Pyrrhos' main goal was to conquer Macedonia but lacked enough funds to pay the necessary mercenaries. So he planned to help Taranto and then move to Sicily and attack Carthage - after winning and conquering southern Italy, he should have had enough money to build an army strong enough to conquer Macedonia.
First Punic war [264-241BC]
The First Punic War (264-241 BC) was the first of a total of three Punic wars fought between Carthage and the Republic of Rome. For 23 years, these two powers have struggled to dominate the western Mediterranean. Carthage, located in North Africa, was the dominant naval power in the Mediterranean at the beginning of the war. But it was Rome, who eventually achieved victory.
Second Punic war [219-202BC]
The Second Punic War was fought between the Romans and the Carthaginians between 218 and 201 BC. The Carthaginian warlord Hannibal of the Barkas family first gave Rome a series of defeats in tactically ingenious battles, which are still featured in military textbooks. Subsequently, the Romans went into a several-year-long wear-and-tear war, gradually eliminating or neutralizing the allies and major colonies of Carthage, and finally, under the leadership of Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus, won the Battle of Zamy. This war finally decided the struggle of both cities to dominate the Mediterranean in favour of Rome.
First Macedonian War [214-205 BC]
The First Macedonian War (214–205 BC) was fought by Rome, allied (after 211 BC) with the Aetolian League and Attalus I of Pergamon, against Philip V of Macedon, contemporaneously with the Second Punic War (218–201 BC) against Carthage. There were no decisive engagements, and the war ended in a stalemate. During the war, Macedon attempted to gain control over parts of Illyria and Greece, but without success. It is commonly thought that these skirmishes in the east prevented Macedon from aiding the Carthaginian general Hannibal in the war with Rome. The Peace of Phoenice (205 BC) formally ended the war.
Second Macedonian War [200-196 BC]
The Second Macedonian War (200–197 BC) was fought between Macedon, led by Philip V of Macedon, and Rome, allied with Pergamon and Rhodes. The result was the defeat of Philip who was forced to abandon all his possessions in southern Greece, Thrace and Asia Minor. During their intervention, and although the Romans declared the "freedom of the Greeks" against the rule from the Macedonian kingdom, the war marked a significant stage in increasing Roman intervention in the affairs of the eastern Mediterranean which would eventually lead to their conquest of the entire region.
Third macedonian war [171-168BC]
The Third Macedonian War (171–168 BC) was a war fought between the Roman Republic and King Perseus of Macedon. In 179 BC King Philip V of Macedon died and was succeeded by his ambitious son Perseus. He was anti-Roman and stirred anti-Roman feelings around Macedonia. Tensions escalated and Rome declared war on Macedon.
Third Punic war [149-146BC]
The Third Punic War (149–146 BC) was the third and last of the Punic Wars fought between the former Phoenician colony of Carthage and the Roman Republic. This war was a much smaller engagement than the two previous Punic Wars and focused on Tunisia, mainly on the Siege of Carthage, which resulted in the complete destruction of the city, the annexation of all remaining Carthaginian territory by Rome, and the death or enslavement of the entire Carthaginian population. The Third Punic War ended Carthage's independent existence.
Jugurthine War [112-106 BC]
The Jugurthine War took place in 112–106 BC, between Rome and Jugurtha of Numidia, a kingdom on the north African coast approximating to modern Algeria. Jugurtha was the nephew and adopted the son of Micipsa, King of Numidia, whom he succeeded on the throne, overcoming his rivals through assassination, war, and bribery. The war constituted an important phase in the Roman subjugation of Northern Africa, but Numidia did not become a Roman province until 46 BC. Following Jugurtha's usurpation of the throne of Numidia, a loyal ally of Rome since the Punic Wars, Rome felt compelled to intervene.
Social War [91-88 BC]
The Social War - also called the Italian War, the War of the Allies or the Marsic War - was a war waged from 91 to 88 BC between the Roman Republic and several of the other cities and tribes in Italy, which prior to the war had been Roman allies for centuries. The Italian allies wanted the Roman citizenship, and the power, influence and the right to vote at Rome itself that came with it. The Romans ignored their demands and refused to grant them citizenship, thus leaving the Italian groups with fewer rights and privileges. This led to a devastating war, which lasted three years and caused many casualties. The war eventually resulted in a Roman victory. However, Rome granted Roman citizenship to all of its Italian allies, to avoid another costly war.
Gallic Wars [58-50 BC]
The Gallic Wars were a series of military campaigns waged by the Roman proconsul Julius Caesar against several Gallic tribes. Rome's war against the Gallic tribes lasted from 58 BC to 50 BC and culminated in the decisive Battle of Alesia in 52 BC, in which a complete Roman victory resulted in the expansion of the Roman Republic over the whole of Gaul (mainly present-day France and Belgium).
Great Roman Civil War [49-45 BC]
The Great Roman Civil War (49–45 BC), also known as Caesar's Civil War, was one of the last politico-military conflicts in the Roman Republic before the establishment of the Roman Empire. It began as a series of political and military confrontations, between Julius Caesar, his political supporters and his legions, against the Optimates, the politically conservative and socially traditionalist faction of the Roman Senate, who were supported by Pompey and his legions.
Rome civil war [37-31 BC]

Dacian Wars [101-106]
The First Roman–Dacian War took place from 101 to 102 AD. The Kingdom of Dacia, under King Decebalus, had become a threat to the Roman Empire and defeated several of Rome's armies during Domitian's reign (81-96). Emperor Trajan was set on riding this threat to Rome's power and in 101 set out determined to defeat Dacia. After a year of heavy fighting, King Decebalus came to terms and accepted an unfavourable peace. When he broke these terms in 105, the Second Dacian War (105 - 106 AD) began.
Markoman wars [166-180]
The Marcomannic Wars were a series of wars lasting over a dozen years from about 166 until 180 AD. These wars pitted the Roman Empire against, principally, the Germanic Marcomanni and Quadi and the Sarmatian Iazyges; there were related conflicts with several other barbarian peoples along both sides of the whole length of the Roman Empire's northeastern European border, the river Danube. The struggle against the Germans and Sarmatians occupied the major part of the reign of Roman emperor Marcus Aurelius
War with Attila and Huns [450-453]
The Huns had maintained good relations with the Western Empire. However, Honoria, sister of the Western Roman Emperor Valentinian III, sent Attila a ring and requested his help to escape her betrothal to a senator. Attila claimed her as his bride and half the Western Roman Empire as dowry. Additionally, a dispute arose about the rightful heir to a king of the Salian Franks. In 451, Attila's forces entered Gaul. A combined army of Roman and Visigoths then defeated the Huns at the Battle of the Catalaunian Plains. The following year, Attila renewed his claims to Honoria and territory in the Western Roman Empire. Leading his army across the Alps and into Northern Italy, he sacked and razed a number of cities. Hoping to avoid the sack of Rome, Emperor Valentinian III sent two envoys and Pope Leo I, who met Attila and obtained from him the promise that he would withdraw from Italy and negotiate peace with the emperor. The new Eastern Roman Emperor Marcian then halted tribute payments to Huns, resulting in Attila planning to attack Constantinople. However, in 453 he died of a haemorrhage on his wedding night.Join us
We believe that there are people with different interests and experiences who could contribute their knowledge and ideas. If you love military history and have experience in historical research, writing articles, editing text, moderating, creating images, graphics or videos, or simply have a desire to contribute to our unique system, you can join us and help us create content that will be interesting and beneficial to other readers.
Find out more