| Název: Name: | Lohner Typ L | Lohner Type L |
| Originální název: Original Name: | Lohner Typ L | |
| Kategorie: Category: | průzkumný/pozorovací letoun | reconnaissance/scout aeroplane |
| Výrobce: Producer: | DD.MM.1914-DD.09.1916 Jacob Lohner & Co., Wien DD.10.1915-DD.MM.1916 Ungarische Flugzeugfabrik AG, Budapest | |
| Období výroby: Production Period: | DD.MM.1914-DD.09.1916 | |
| Vyrobeno kusů: Number of Produced: | 108: - 1914: 3 - 1915: 60 - 1916: 45 | |
| První vzlet: Maiden Flight: | DD.MM.1915 | |
| Osádka: Crew: | 2 | |
| Základní charakteristika: Basic Characteristics: | ||
| Vzlet a přistání: Take-off and Landing: | CTOL - konvenční vzlet a přistání | CTOL - conventional take-off and landing |
| Uspořádání křídla: Arrangement of Wing: | dvouplošník | biplane |
| Uspořádání letounu: Aircraft Concept: | klasické | conventional |
| Podvozek: Undercarriage: | jiný | other |
| Přistávací zařízení: Landing Gear: | člunový trup | flying boat |
| Technické údaje: Technical Data: | ||
| Hmotnost prázdného letounu: Empty Weight: | 1150 kg | 2535 lb |
| Vzletová hmotnost: Take-off Weight: | 1700 kg | 3748 lb |
| Maximální vzletová hmotnost: Maximum Take-off Weight: | ? kg | ? lb |
| Rozpětí: Wingspan: | 16.20 m | 53ft 1,79in |
| Délka: Length: | 10.26 m | 33ft 7,93in |
| Výška: Height: | 3.85 m | 12ft 7,56in |
| Plocha křídla: Wing Area: | 53.0 m2 | 570.49 ft2 |
| Plošné zatížení: Wing Loading: | ? kg/m2 | ? lb/ft2 |
| Pohon: Propulsion: | ||
| Kategorie: Category: | pístový | piston |
| Počet motorů: Number of Engines: | 1 | |
| Typ: Type: | Austro-Daimler AD6 série 17000 o výkonu 118 kW/160 k | Austro-Daimler AD6 series 17000, power 158 hp |
| Objem palivových nádrží: Fuel Tank Capacity: | 200 l | 44 Imp gal / 53 US gal |
| Výkony: Performance: | ||
| Maximální rychlost: Maximum Speed: | 105 km/h v ? m | 65.2 mph in ? ft |
| Cestovní rychlost: Cruise Speed: | ? km/h v ? m | ? mph in ? ft |
| Rychlost stoupání: Climb Rate: | ? m/s | ? ft/min |
| Čas výstupu na výšku: Time to Climb to: | 13,75 min do 1000 m | 13,75 min to 3281 ft |
| Operační dostup: Service Ceiling: | 2500 m | 8202 ft |
| Dolet: Range: | 600 km | 373 mi |
| Maximální dolet: Maximum Range: | ? km | ? mi |
| Výzbroj: Armament: | 1x kulomet pro pozorovatele až 200 kg bomb | 1x flexible machine gun for observer 441 lb of bombs |
| Uživatelské státy: User States: | | |
| Poznámka: Note: | - | - |
| Zdroje: Sources: | http://cs.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lohner_L http://www.insigniamag.com/lohn.html mainescenery.proboards.com http://www.aeronautica.difesa.it/.../LohnerL-127.aspx http://www.bizzoco.it/lohner.html | |
Lohner L
Lohner L
The Lohner L was a reconnaissance flying boat produced in Austria-Hungary during World War I. It was a twin-truss monoplane of the typical layout of contemporary flying boats - with the engine suspended in a pusher arrangement on struts in the interwing gap. The pilot and observer sat side by side in an open cockpit and the upper and lower wings could be folded back.
Circumstances of origin
The Austro-Hungarian Navy had already shown more confidence in the capabilities of seaplanes than its German ally before the outbreak of World War I. During these years, many types saw the light of day at the firm of Jacob Lohner of Vienna, founded by Heinrich Lohner in March 1821. Their first aircraft was built as early as 1910 under the direction of the pioneering aviator and designer Rittmeister Hans Umlauf, and the designer Leopold Bayer (who became Lohner's technical director in 1916). To supply aircraft for both the army and the navy, they created several types before the outbreak of war, including a seaplane with an arrow wing and types E, R, M. Among others of the many, mention should be made of the type L, a two-seat reconnaissance, patrol and bombing machine, widely used in the Adriatic Sea area.
The Austrian Navy pioneered the use of these instruments of war as early as 1913, during the so-called Balkan Crisis: only after this did the first three seaplanes Donnet-Leveque of French design arrive at the naval base in Kotor, followed by other types of foreign origin, such as the Curtiss and Etrich machines.
By 1914, the Lohner factory patented its biplane and central boat hull design, which would appear in a future series of seaplanes that would battle in the skies of the Adriatic Sea until the end of the war in 1918.
The first products of series production were the E type, with the 85 horsepower Hiero engine, of which a total of forty were built between 1914 and 1915.
An obvious step forward, especially in terms of performance, was the Type L, the most widely used of the Lohner aircraft, with similar dimensions to the Type E but with a more powerful engine, usually of the Austro-Daimler type with 140 hp. In November 1914, the Lohner factory accepted an order for six new seaplanes from the Naval Air Service. In collaboration with engineers and technicians from the arsenal in the port of Pula, a new Type L was designed, which was a development of the previous Types M and Mk. The first two Type L machines were ready for delivery in late 1914 and were assigned the serial numbers L40 and L41, both fitted with 150hp Rapp engines. Further development then proceeded rapidly, with the L42, L43, L44 and L45 following shortly afterwards. These machines were already fitted with water-cooled inline six-cylinder engines of 140hp. These six machines formed the pre-production range which evolved into the following series: the Type L (L46-L51 series), Type T (L52-L57 series), Type Te (L58-L119 series) and Type T1 (L120-L143 series). A total of 104 flying boats (2. p.) of these types were thus produced. They differed from the first six (L40-L45) mainly in the type of cabin used, these aircraft having glass windows in the front, sides and top of the cockpit.
Design and construction
The basis of the design was the E model, the L type essentially a more powerful version of it. It was the successful Type L that became the model for many successors. Apart from licensed production by UFAG, the L machines provided the basis for designs by other major manufacturers. In Germany, a modified version was produced by Hansa-Brandenburg under the designation FB (Flugboot ) as its first ever flying boat, while in Italy a salvage example served as a model for its own production.
Technical description
The Lohner L, like the other Austrian seaplanes, was a truss biplane with a lower wing span smaller than the upper (this concept was referred to as a one-and-a-half-plane), the lower wing was rectangular in plan with slightly rounded ends, with a slight rise of about 3' and a very obvious arrow angle, about 10°. The two wings were connected by numerous struts of variable number (6 pairs on the L model). Only the upper wing was fitted with ailerons extending beyond the trailing edge.
Particular care was taken in the construction of the fuselage (all-wood construction, as well as other parts of the aircraft), which tapered significantly towards the nose, ensuring good nautical performance, as in fast powerboats, without compromising aerodynamic properties. The tail surfaces were welded from metal tubes and covered with plywood, the moving parts with canvas.
The crew, consisting of two persons seated side by side, which facilitated their communication with each other, was placed in the bow, protected by a not very high protective glass, with the pilot on the left and the observer on the right: in front of the observer, a single non-moving machine gun, usually of the Schwarzlose type, was placed on a support. In addition to this armament, Lohner seaplanes carried a war load consisting of bombs (from 5 or 50 kilos) or anti-submarine depth charges of about 200 kilos, secured externally on the sides of the fuselage.
The engine was usually an Austro-Daimler, inline six-cylinder of 140 hp, or a Hiero Warchalowski of similar power, mounted on a trio of N-shaped struts, fitted with a pusher propeller. The engine gearbox was uncovered and thus formed a very distinctive feature; the honeycomb radiator was located at the front of the engine, slightly extended upwards. The fuel tank (with a total capacity of 200 litres) was located on the fuselage behind the cockpit.
The instrumentation, of course only basic, was arranged on a small dashboard in front of the two-man crew. In addition, a certain number of Austrian seaplanes were equipped with an apparatus for wireless telegraphy of the Telefunken system, powered by an alternating current generator, driven by the engine; however, very few aircraft were equipped with a receiving station, Part of the equipment included an anchor located in the fuselage. Austro-Hungarian seaplanes were also equipped with a searchlight manually operated by an observer, who in addition had one supply of Véra signal pistol and with a supply of signal flares in a metal case.
A primitive bomb sight consisting of a square structure, complete with wind drift correction indicators, was also found on various examples captured by the Italians.
Colouring
The Flying Boat L had a plywood hull, with the nosecones painted clear lacquer and covered with canvas. Everything was left in a natural finish. The fuselage, typical of a naval aircraft, was repainted with a gloss oil varnish. Serial L40s appeared with white paint on the fuselage sides. The national markings are typical of the period from August 1914 to January 1916 : the outer wing tips, elevators and rudder have red/white/Red Naval Air Service stripes. The white stripe on the rudder also bears the Austro-Hungarian coat of arms, with the royal crown and shield edged in gold or yellow. The shield contains horizontal red/white/red stripes.
Operational history
Lohner seaplanes saw extensive use before World War I and throughout their lifetime, and were not outdone after the war, serving for several more years.
In addition to their routine service, the L machines are distinguished by several firsts:
- The Lohner L seaplane from the Kumbor base immediately after the Austro-Hungarian declaration of war on Serbia and Montenegro had already patrolled and photographed the artillery positions of the Montenegrins between 28 July 1914 and 2 August 1914. This action represents the first use of the aircraft in World War I.
- During the war, on 16 September 1916, the crews of Lohner L 132 piloted by Lieutenant Commander Dimitrij Konjović and Lohner L 135 piloted by Officer Walter Zelezny on regular reconnaissance missions found the French submarine "Foucault" near Kotor, which they attacked with bombs. The submarine was damaged in the attack and her crew had to abandon her. Lohner landed at sea, captured two French officers and transported them to the Kumbor base. Other crew members were rescued by an Austro-Hungarian torpedo boat. This was the first sinking of a submarine from the air in the history of aviation.
Variants
Lohner L
Lohner Tl - company designation for machines with a lightweight airframe
Lohner Te - another company designation for lightweight machines
Lohner R - photo-research version
Lohner S - training aircraft
Hansa-Brandenburg FB - German licensed version
Macchi L.1- Italian version, Fiat machine gun, Isotta-Fraschini V.4A engine
The Lohner L was a reconnaissance flying boat produced in Austria-Hungary during World War I. It was a twin-truss monoplane of the typical layout of contemporary flying boats - with the engine suspended in a pusher arrangement on struts in the interwing gap. The pilot and observer sat side by side in an open cockpit and the upper and lower wings could be folded back.
Circumstances of origin
The Austro-Hungarian Navy had already shown more confidence in the capabilities of seaplanes than its German ally before the outbreak of World War I. During these years, many types saw the light of day at the firm of Jacob Lohner of Vienna, founded by Heinrich Lohner in March 1821. Their first aircraft was built as early as 1910 under the direction of the pioneering aviator and designer Rittmeister Hans Umlauf, and the designer Leopold Bayer (who became Lohner's technical director in 1916). To supply aircraft for both the army and the navy, they created several types before the outbreak of war, including a seaplane with an arrow wing and types E, R, M. Among others of the many, mention should be made of the type L, a two-seat reconnaissance, patrol and bombing machine, widely used in the Adriatic Sea area.
The Austrian Navy pioneered the use of these instruments of war as early as 1913, during the so-called Balkan Crisis: only after this did the first three seaplanes Donnet-Leveque of French design arrive at the naval base in Kotor, followed by other types of foreign origin, such as the Curtiss and Etrich machines.
By 1914, the Lohner factory patented its biplane and central boat hull design, which would appear in a future series of seaplanes that would battle in the skies of the Adriatic Sea until the end of the war in 1918.
The first products of series production were the E type, with the 85 horsepower Hiero engine, of which a total of forty were built between 1914 and 1915.
An obvious step forward, especially in terms of performance, was the Type L, the most widely used of the Lohner aircraft, with similar dimensions to the Type E but with a more powerful engine, usually of the Austro-Daimler type with 140 hp. In November 1914, the Lohner factory accepted an order for six new seaplanes from the Naval Air Service. In collaboration with engineers and technicians from the arsenal in the port of Pula, a new Type L was designed, which was a development of the previous Types M and Mk. The first two Type L machines were ready for delivery in late 1914 and were assigned the serial numbers L40 and L41, both fitted with 150hp Rapp engines. Further development then proceeded rapidly, with the L42, L43, L44 and L45 following shortly afterwards. These machines were already fitted with water-cooled inline six-cylinder engines of 140hp. These six machines formed the pre-production range which evolved into the following series: the Type L (L46-L51 series), Type T (L52-L57 series), Type Te (L58-L119 series) and Type T1 (L120-L143 series). A total of 104 flying boats (2. p.) of these types were thus produced. They differed from the first six (L40-L45) mainly in the type of cabin used, these aircraft having glass windows in the front, sides and top of the cockpit.
Design and construction
The basis of the design was the E model, the L type essentially a more powerful version of it. It was the successful Type L that became the model for many successors. Apart from licensed production by UFAG, the L machines provided the basis for designs by other major manufacturers. In Germany, a modified version was produced by Hansa-Brandenburg under the designation FB (Flugboot ) as its first ever flying boat, while in Italy a salvage example served as a model for its own production.
Technical description
The Lohner L, like the other Austrian seaplanes, was a truss biplane with a lower wing span smaller than the upper (this concept was referred to as a one-and-a-half-plane), the lower wing was rectangular in plan with slightly rounded ends, with a slight rise of about 3' and a very obvious arrow angle, about 10°. The two wings were connected by numerous struts of variable number (6 pairs on the L model). Only the upper wing was fitted with ailerons extending beyond the trailing edge.
Particular care was taken in the construction of the fuselage (all-wood construction, as well as other parts of the aircraft), which tapered significantly towards the nose, ensuring good nautical performance, as in fast powerboats, without compromising aerodynamic properties. The tail surfaces were welded from metal tubes and covered with plywood, the moving parts with canvas.
The crew, consisting of two persons seated side by side, which facilitated their communication with each other, was placed in the bow, protected by a not very high protective glass, with the pilot on the left and the observer on the right: in front of the observer, a single non-moving machine gun, usually of the Schwarzlose type, was placed on a support. In addition to this armament, Lohner seaplanes carried a war load consisting of bombs (from 5 or 50 kilos) or anti-submarine depth charges of about 200 kilos, secured externally on the sides of the fuselage.
The engine was usually an Austro-Daimler, inline six-cylinder of 140 hp, or a Hiero Warchalowski of similar power, mounted on a trio of N-shaped struts, fitted with a pusher propeller. The engine gearbox was uncovered and thus formed a very distinctive feature; the honeycomb radiator was located at the front of the engine, slightly extended upwards. The fuel tank (with a total capacity of 200 litres) was located on the fuselage behind the cockpit.
The instrumentation, of course only basic, was arranged on a small dashboard in front of the two-man crew. In addition, a certain number of Austrian seaplanes were equipped with an apparatus for wireless telegraphy of the Telefunken system, powered by an alternating current generator, driven by the engine; however, very few aircraft were equipped with a receiving station, Part of the equipment included an anchor located in the fuselage. Austro-Hungarian seaplanes were also equipped with a searchlight manually operated by an observer, who in addition had one supply of Véra signal pistol and with a supply of signal flares in a metal case.
A primitive bomb sight consisting of a square structure, complete with wind drift correction indicators, was also found on various examples captured by the Italians.
Colouring
The Flying Boat L had a plywood hull, with the nosecones painted clear lacquer and covered with canvas. Everything was left in a natural finish. The fuselage, typical of a naval aircraft, was repainted with a gloss oil varnish. Serial L40s appeared with white paint on the fuselage sides. The national markings are typical of the period from August 1914 to January 1916 : the outer wing tips, elevators and rudder have red/white/Red Naval Air Service stripes. The white stripe on the rudder also bears the Austro-Hungarian coat of arms, with the royal crown and shield edged in gold or yellow. The shield contains horizontal red/white/red stripes.
Operational history
Lohner seaplanes saw extensive use before World War I and throughout their lifetime, and were not outdone after the war, serving for several more years.
In addition to their routine service, the L machines are distinguished by several firsts:
- The Lohner L seaplane from the Kumbor base immediately after the Austro-Hungarian declaration of war on Serbia and Montenegro had already patrolled and photographed the artillery positions of the Montenegrins between 28 July 1914 and 2 August 1914. This action represents the first use of the aircraft in World War I.
- During the war, on 16 September 1916, the crews of Lohner L 132 piloted by Lieutenant Commander Dimitrij Konjović and Lohner L 135 piloted by Officer Walter Zelezny on regular reconnaissance missions found the French submarine "Foucault" near Kotor, which they attacked with bombs. The submarine was damaged in the attack and her crew had to abandon her. Lohner landed at sea, captured two French officers and transported them to the Kumbor base. Other crew members were rescued by an Austro-Hungarian torpedo boat. This was the first sinking of a submarine from the air in the history of aviation.
Variants
Lohner L
Lohner Tl - company designation for machines with a lightweight airframe
Lohner Te - another company designation for lightweight machines
Lohner R - photo-research version
Lohner S - training aircraft
Hansa-Brandenburg FB - German licensed version
Macchi L.1- Italian version, Fiat machine gun, Isotta-Fraschini V.4A engine
Reklama
Lohner L.
| Period | - |
| Producer | - |
| Type | - |
| Camouflage | - |
| Country | - |
| Pilot | - |
| Production No. | - |
| Serial No. / Evidence No. | - |
| Tactical Marking / Imatriculation | - |
| Name | - |
| Unit | - |
| Base | - |
| Date (DD.MM.RRRR) | - |
| Author | - |
| Print size / 300 DPI | - |
| Published with authors permit | - |
| Author Website | - |
Lohner L (L127)
This piece was delivered to the imperial war navy in June 1916. By the end of 1917 he participated in raids on the Italian positions. Later, he was bázován at the base in Lussinu, where he carried out reconnaissance flights over dalmátským the coast and where he was eventually 3. June, 1918, in the early morning, stolen two sailors of Italian origin. You with him přeleti Adriatic sea and landed in the Italian waters near Fana. Here is the saw the members 2. armored train (2° Treno Armato), who aircraft identified and captured and its crew. In the following hours they were deployed on the aircraft FBA maritime pilots officers Aldo Pellegrini and Alberto Briganti from the base Ancona to fly over a captured machine. In the hangar at Ancona the machine also spent the rest of the war.
Among other things, together with another machine allegedly participated in a raid on the city of Bari 11. August 1918, in which were the two machines are forced to land, and even with the crews captured. The machines were then returned, the crew remained in captivity. In the air raid were dropped four bombs, two of which struck the city and killed two women, one old and one baby and injuring eight other people.
In 1988, after a series of repairs, the long restaurant, when there were some pieces replaced with new materials, this machine was finally taken to the museum of the history of military aviation in Vigna di Valle (Bracciano) on lake Bracciano (Museo storico dell'Aeronautica Militare di Vigna di Valle). Here is today exposed as the only machine of this type in the world.
Source:
http://www.bizzoco.it/lohner.html
materials of the museum.
vlastní foto
vlastní foto
vlastní foto
This piece was delivered to the imperial war navy in June 1916. By the end of 1917 he participated in raids on the Italian positions. Later, he was bázován at the base in Lussinu, where he carried out reconnaissance flights over dalmátským the coast and where he was eventually 3. June, 1918, in the early morning, stolen two sailors of Italian origin. You with him přeleti Adriatic sea and landed in the Italian waters near Fana. Here is the saw the members 2. armored train (2° Treno Armato), who aircraft identified and captured and its crew. In the following hours they were deployed on the aircraft FBA maritime pilots officers Aldo Pellegrini and Alberto Briganti from the base Ancona to fly over a captured machine. In the hangar at Ancona the machine also spent the rest of the war.
Among other things, together with another machine allegedly participated in a raid on the city of Bari 11. August 1918, in which were the two machines are forced to land, and even with the crews captured. The machines were then returned, the crew remained in captivity. In the air raid were dropped four bombs, two of which struck the city and killed two women, one old and one baby and injuring eight other people.
In 1988, after a series of repairs, the long restaurant, when there were some pieces replaced with new materials, this machine was finally taken to the museum of the history of military aviation in Vigna di Valle (Bracciano) on lake Bracciano (Museo storico dell'Aeronautica Militare di Vigna di Valle). Here is today exposed as the only machine of this type in the world.
Source:
http://www.bizzoco.it/lohner.html
materials of the museum.
| Period | - |
| Producer | - |
| Type | - |
| Camouflage | - |
| Country | - |
| Pilot | - |
| Production No. | - |
| Serial No. / Evidence No. | - |
| Tactical Marking / Imatriculation | - |
| Name | - |
| Unit | - |
| Base | - |
| Date (DD.MM.RRRR) | - |
| Author | - |
| Print size / 300 DPI | - |
| Published with authors permit | - |
| Author Website | - |
vlastní foto
| Period | - |
| Producer | - |
| Type | - |
| Camouflage | - |
| Country | - |
| Pilot | - |
| Production No. | - |
| Serial No. / Evidence No. | - |
| Tactical Marking / Imatriculation | - |
| Name | - |
| Unit | - |
| Base | - |
| Date (DD.MM.RRRR) | - |
| Author | - |
| Print size / 300 DPI | - |
| Published with authors permit | - |
| Author Website | - |
vlastní foto
| Period | - |
| Producer | - |
| Type | - |
| Camouflage | - |
| Country | - |
| Pilot | - |
| Production No. | - |
| Serial No. / Evidence No. | - |
| Tactical Marking / Imatriculation | - |
| Name | - |
| Unit | - |
| Base | - |
| Date (DD.MM.RRRR) | - |
| Author | - |
| Print size / 300 DPI | - |
| Published with authors permit | - |
| Author Website | - |
vlastní foto
This post has not been translated to English yet. Please use the TRANSLATE button above to see machine translation of this post.
| Period | World War One / The Great War [1914-1918] |
| Producer | Lohner |
| Type | Lohner L |
| Camouflage | Standardní vojenská |
 Bílá / White Bílá / White Dřevo / Wood Dřevo / Wood Plátno / Fabric Plátno / Fabric Červená / Red Červená / Red |
|
| Country |  |
| Pilot | Banfield, Gottfried von |
| Production No. | - |
| Serial No. / Evidence No. | L 16 |
| Tactical Marking / Imatriculation | - |
| Name | - |
| Unit | - |
| Base | - |
| Date (DD.MM.RRRR) | DD.06.1916 |
| Author | Zbyněk Válka |
| Print size / 300 DPI | A4 |
| Published with authors permit | Published with authors permit |
| Author Website | - |
Hydroavion Lohner L 16, Terst, léto 1916. Jde o osobní stroj Linienschiffsleutnanta (kapitán) Gottfrieda Freiher von Banfield, nejúspěšnějšího rakousko-uherského námořního letce. L 16 byl speciálně pro Banfielda přestavěn firmou Albatros na jednomístný stíhací obranný člun "Abwehrflugzeuge". Letoun byl vybaven motorem Hiero o výkonu 140 ks a pevným vzduchem chlazeným kulometem Schwarzlose s perforovaným pláštěm původně vodního chladiče. Šlo o nejúspěšnější Banfieldův stroj - dosáhl na něm 6 potvrzených a 3 nepotvrzených sestřelů. Letoun létal v barvě materiálu s výjimkou červeno-bílých-červených pruhů na křídlech a ocasních plochách. Na křídlech výsostné označení typu "B", bez černých lemů a a bílých podkladových čtverců, v 6 pozicích (horní křídlo z obou stran, spodní pouze zespodu). Erb na SOP je zlatě lemovaný a stínovaný. Kříž na přídi se při bočním pohledu jeví jako asymetrický; je dokonale souměrný při čelním pohledu.
Published with authors permit
Reklama
This post has not been translated to English yet. Please use the TRANSLATE button above to see machine translation of this post.
| Period | World War One / The Great War [1914-1918] |
| Producer | UFAG |
| Type | |
| Camouflage | Standardní vojenská |
 Plátno / Fabric Plátno / Fabric Dřevo / Wood Dřevo / Wood |
|
| Country |  |
| Pilot | - |
| Production No. | - |
| Serial No. / Evidence No. | L 65 |
| Tactical Marking / Imatriculation | L 65 |
| Name | - |
| Unit | - |
| Base | - |
| Date (DD.MM.RRRR) | 03.04.1916 |
| Author | Zbyněk Válka |
| Print size / 300 DPI | A4 |
| Published with authors permit | Published with authors permit |
| Author Website | - |
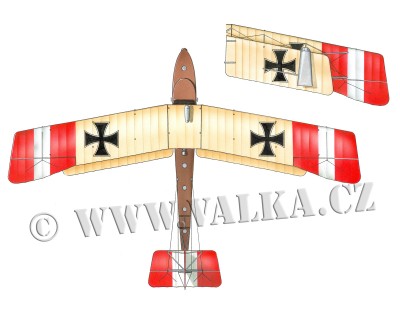
Tento Lohner typu Te patřil k třídě Lohnerů L a byl vyroben firmou UFAG. 3. dubna 1916 se posádce Lschlt. Hugo Stenta a Koch podařilo zachránit posádku havarovaného člunu L70, která se zase pokoušela zachránit letce z L71. Stroj v barvě materiálu, kříže jsou umsítěny na obou stranách nosných ploch, avšak ne v předpisových bílých plochách, nýbrž jen opatřené lemem.
Published with authors permit
| Period | World War One / The Great War [1914-1918] |
| Producer | UFAG |
| Type | |
| Camouflage | Standardní vojenská |
 Plátno / Fabric Plátno / Fabric Dřevo / Wood Dřevo / Wood |
|
| Country |  |
| Pilot | - |
| Production No. | - |
| Serial No. / Evidence No. | L 65 |
| Tactical Marking / Imatriculation | L 65 |
| Name | - |
| Unit | - |
| Base | - |
| Date (DD.MM.RRRR) | 03.04.1916 |
| Author | Zbyněk Válka |
| Print size / 300 DPI | A4 |
| Published with authors permit | Published with authors permit |
| Author Website | - |
Published with authors permit
Join us
We believe that there are people with different interests and experiences who could contribute their knowledge and ideas. If you love military history and have experience in historical research, writing articles, editing text, moderating, creating images, graphics or videos, or simply have a desire to contribute to our unique system, you can join us and help us create content that will be interesting and beneficial to other readers.
Find out more