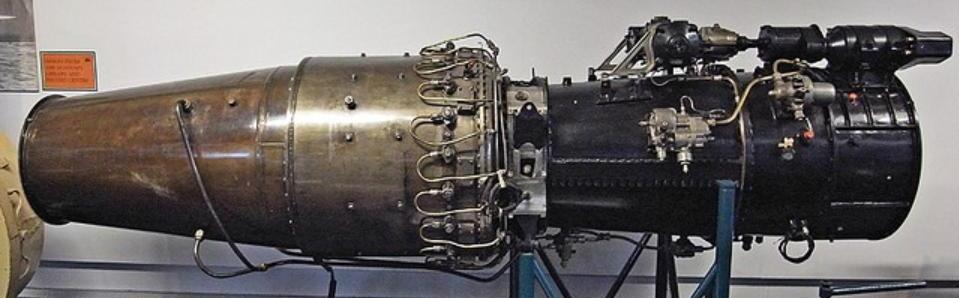
Turbojets

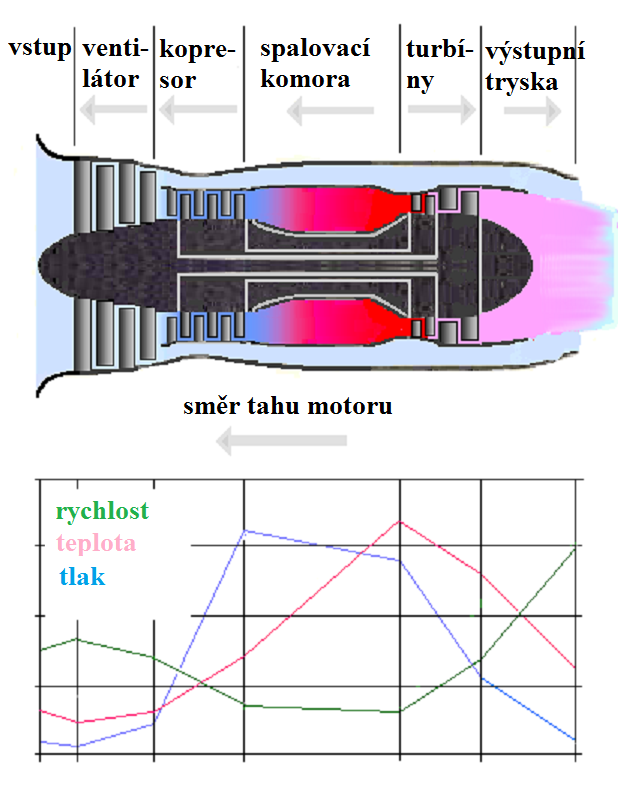
Development of World War II jet engines at Heinkel
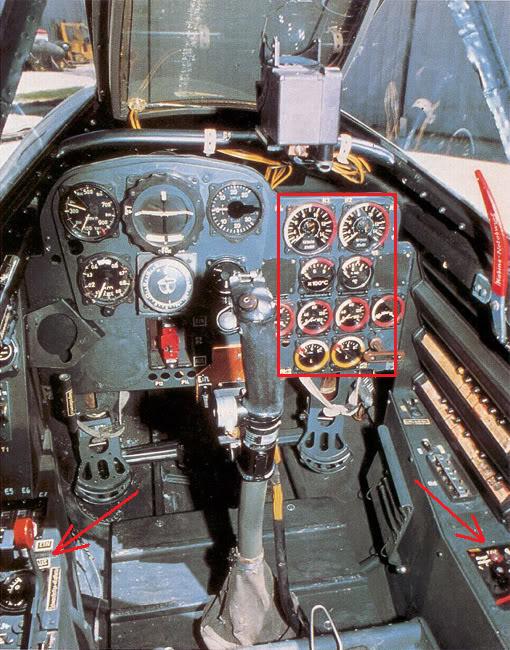
Junkers Jumo 004 B-1 jet engine

Starting the first German jet engines

TR-1 jet engine
Even before A.M. Ljulka started working on the jet engine, similar work was done in England and Germany, that the first jet engines were tested here in 1937 and the first flight of the jet engine took place in Germany in 1939. But all this happened in deep secrecy. So A.M. Ljulka went this route alone and is rightly considered the founder of the development of jet engines in the USSR.

Czech Republic / Czechoslovakia (CZE / CZK)

People's Republic of China (CHN)
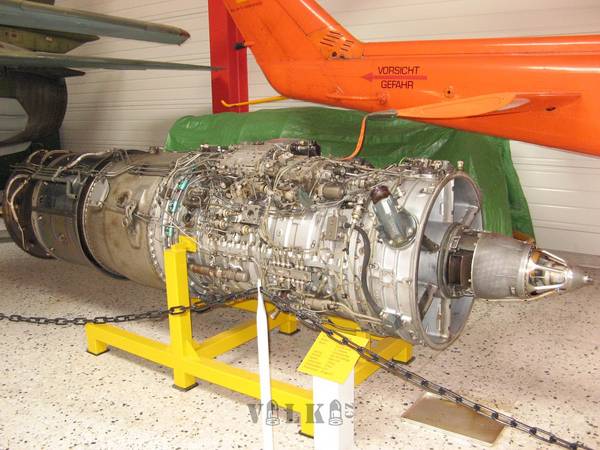

France (FRA)

Japan (JPN)
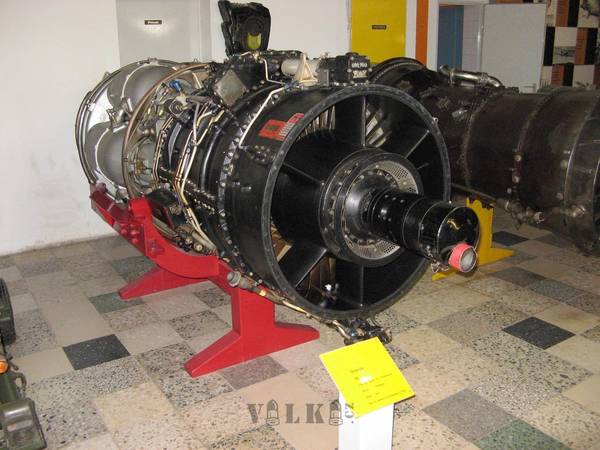

Canada (CAN)

Germany (DEU)

Poland (POL)
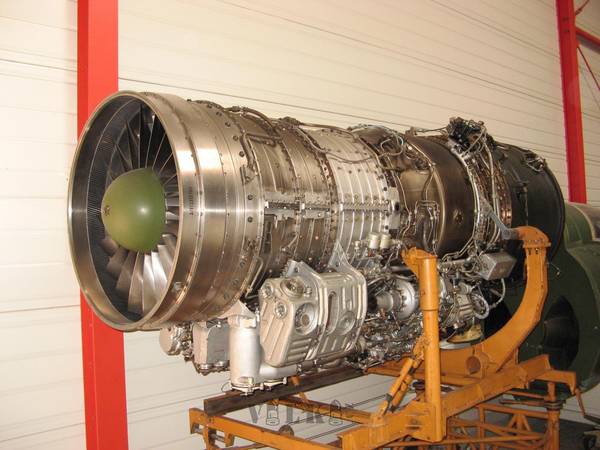

Russia / Soviet Union (RUS / SOV)
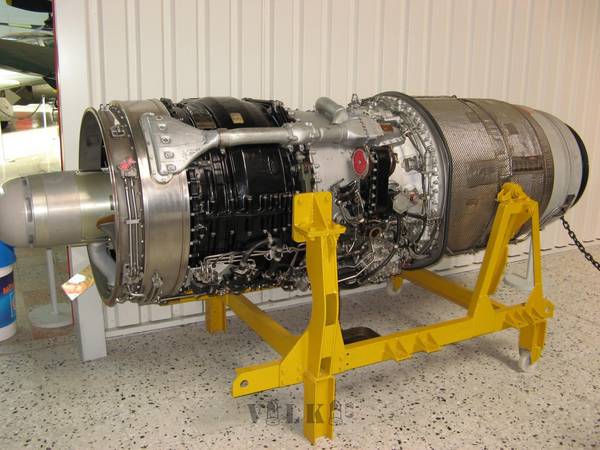

United Kingdom (GBR)

United States of America (USA)

Sweden (SWE)

Ukraine (UKR)
Join us
We believe that there are people with different interests and experiences who could contribute their knowledge and ideas. If you love military history and have experience in historical research, writing articles, editing text, moderating, creating images, graphics or videos, or simply have a desire to contribute to our unique system, you can join us and help us create content that will be interesting and beneficial to other readers.
Find out more