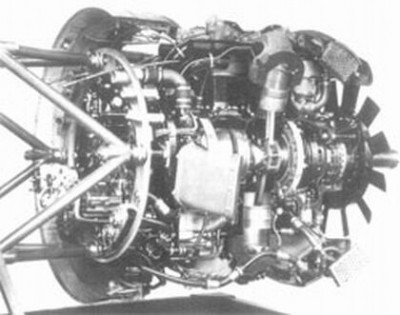
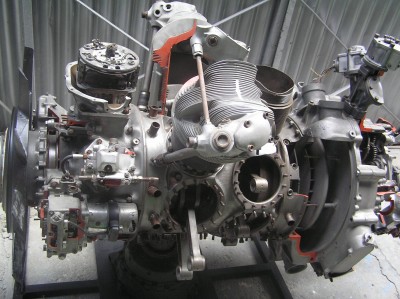
| Název: Name: | BMW 801 D-2 | BMW 801 D-2 |
| Originální název: Original Name: | BMW 801 D-2 | |
| Kategorie: Category: | hvězdicový motor | radial engine |
| Výrobce: Producer: | Bayerische Motor Werke Flugmotorenbau G.m.b.H., München | |
| Období výroby: Production Period: | DD.MM.1942-DD.MM.1945 | |
| Vyrobeno kusů: Number of Produced: | ? | |
| Prototyp vyroben: Prototype Built: | DD.MM.1941 | |
| Použití: Use: | Focke-Wulf Fw-190 A, F a G, Heinkel He 177 A-8 a A-10, Junkers Ju 88 G a R Junkers Ju 188 Junkers Ju 290 Messerschmitt Me 264 | |
| Technické údaje: Technical Data: | ||
| Počet válců: Number of Cylinders: | 14 | |
| Hmotnost: Weight: | 1010 kg | 2227 lb |
| Celková délka: Overall Length: | 2006 mm | 6ft 6,98in |
| Celková šířka / Průměr: Overall Width / Diameter: | 1290 mm | 4ft 2,78in |
| Celková výška: Overall Height: | - mm | - |
| Vrtání: Bore: | 156 mm | 6,14in |
| Zdvih: Stroke: | 156 mm | 6,14in |
| Zdvihový objem: Swept Volume: (l/cu in) | 41,81 l | 2551.4 cu in |
| Palivo: Fuel: | letecký benzín C3 s oktanovým číslem 100 (96) - (C3-Treibstoff mit 100 Oktan) | Gasoline C3 with octane number 100 (C3-Treibstoff mit 100 Oktan) |
| Příprava palivové směsi: Carburation or Injection: | přímý vstřik - vysokotlaké vstřikování | Hight pressure fuel injection |
| Kompresní poměr: Compression Ratio: | 7,2 : 1 | 7,2 : 1 |
| Plnění válců: Mixture Charging: | Přeplňování - jednostupňový odstředivý dvourychlostní mechanický kompresor. | Supercharger: Gear-driven single-stage twin-speed centrifugal supercharger. |
| Chlazení: Cooling: | vzduchem - nucené | Forced Air-cooled |
| Výkony: Performance: | ||
| Výkon: Power: | 1272 kW při 2700 ot/min | 1705.8 bhp at 2700 rpm |
| Poznámka: Note: | Výkony: vzletový: 1 272 kW (1 730 k) při 2 700 ot/min a plnícím tlaku 1,42 barů (1 065 mm Hg) po dobu 3 min. Bojový trvalý: I. převodový stupeň kompresoru: 1 118 kW (1 520 k) v h= 700 m II. převodový stupeň kompresoru: 971 kW (1 320 k) v h= 5 300 m. bojový s MW50 1 471 kW (2 000 k) v malých a středních výškách Zařízení umožnilo vstřik vody a metanolu v poměru 50/50%. Ventilový rozvod OHV, jeden sací a jeden výfukový ventil (chlazený sodíkovým jádrem) na válec. | Take-off power: 1,705 hp at 2,700 rpm, boosted +20.595 psi Combat power pernament: 1,499 hp at 2,400 rpm at 2,297 ft with rated low blower and 1,302 hp at 2,400 rpm at 17,388 ft with rated high blower. Combat power with MW50: 1,973 hp at 2,700 rpm at low and medium altitudes. Valvetrain: One intake and one sodium-cooled exhaust valve per cylinder. |
| Zdroje: Sources: | Heinz J. Nowarra, Die Deutsche Luftrüstung 1933-1945, Band 4, Koblenz, Bernard & Graeffe Verlag, 1993, ISBN 3-7637-5468-7. http://www.456fis.org/BMW_801_ENGINE.htm http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/BMW_801 www.tighar.org http://www.7-forum.com/.../90-Jahre-BMW-%E2%80%93-Markenzeichen-der-Innovat-1554.html www.warbirdsresourcegroup.org www.warbirdsresourcegroup.org http://www.economicexpert.com/a/BMW:801.html inter.action.free.fr archiv autora | |
BMW 801 D-2
Engine components
Kommandogerät
The engine was equipped with a device called the Kommandogerät, which was essentially a mechanical-hydraulic-electrical control unit that controlled the engine's boost pressure, ignition advance, compressor gear shift, fuel quantity, propeller blade angle of attack, engine speed with respect to engine mode, flight altitude, cylinder head temperature, and most importantly, maintained a constant propeller speed. This device made the control of the aeroplane as easy as possible, with the pilot operating only the throttle stick.
MW50
The MW50 device could be fitted to this type of engine, which allowed the injection of a mixture of water and methanol (1:1 or, hence the name, 50/50%) into the already compressed air just behind the compressor. This mixture quickly evaporated here, cooling the compressed air, and this led to a reciprocal drop in pressure. This compressed air pressure, in turn, limited the compressor performance by creating back pressure. Thus, by reducing the back pressure, the compressor could operate at a higher efficiency and could (and did) supply more air to the engine. The equipment was used at low and medium altitudes.
Ignition
To ignite the compressed air-fuel mixture, a BOSCH ZM 14 double magneto was used, which was mounted on the reducer housing. In each cylinder there were two two-electrode spark plugs of type BOSCH DW 240 ET 7 or Siemens 35 FU14.
Sources used:
Heinz J. Nowarra, Die Deutsche Luftrüstung 1933-1945, Band 4, Koblenz, Bernard & Graeffe Verlag, 1993, ISBN 3-7637-5468-7.
http://www.456fis.org/BMW_801_ENGINE.htm
http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/BMW_801
www.tighar.org
www.warbirdsresourcegroup.org
www.warbirdsresourcegroup.org
http://www.economicexpert.com/a/BMW:801.html
author archive
Reklama
Join us
We believe that there are people with different interests and experiences who could contribute their knowledge and ideas. If you love military history and have experience in historical research, writing articles, editing text, moderating, creating images, graphics or videos, or simply have a desire to contribute to our unique system, you can join us and help us create content that will be interesting and beneficial to other readers.
Find out more