
brano
Branislav Juhász
- Date of registration : 14.01.2004
- Last time active : 27.04.2024
- Posts count : 6.223
- Fact posts : 4.579
- Find all posts of user
- Personal photogallery
Articles


2 cm FlaK 30 auf Selbstfahrlafette (Sd.Kfz.10/4)
Army and Luftwaffe units evaluated this vehicle very positively and formed an integral part of anti-aircraft units throughout World War II.

2 cm FlaK 38 auf Schützenpanzerwagen (Sd.Kfz.251)
This anti-aircraft version of the Sd.Kfz. 251 was developed for the anti-aircraft defence needs of Luftwaffe units. The weapon used was the 2 cm Flak 38. In order to rotate the weapon through its full 360° range, extensive modifications had to be made to the design of the flanks. The side armour was cut out and new hinged folding armoured side plates were fitted in its place. A small series of such vehicles were produced, about which more detailed information is lacking. The number of machines produced was small, only 18 were armed with them. Batterie Flak-Rgt. Hermann Göring. The last vehicles reached service sometime by 4-5/1943.

2 cm Flak 38 auf Selbstfahrlafette (Sd.Kfz.10/5)
A modification of the original Sd.Kfz.10 / 4 created a new version. The modification concerned the effort to replace the primary weapon with a 2 cm Flak 30 cannon with a new and more powerful 2 cm Flak 38 cannon.

2 cm FlaK 38 auf Selbstfahrlafette Zgkw.3t (Sd.Kfz.11/1)
At the turn of 1943/44, this anti-aircraft modification was created on the chassis H kl 6p, ie half-track chassis weight category 3 tons, which formed a platform of armored personnel carriers Sd.Kfz.251 and since 1943 there was an effort to unify platforms and use Hkl 6p for classic unarmored tractors. Sd.Kfz.11).

2cm Flakvierling 38 auf Fahrgestell PzKpfw.IV

3 cm Mk 103 auf Grille M
At the end of 1944, a modification of the self-propelled gun Grille Ausf.M using the chassis PzKpfw.38 (t) was ordered. Instead of a 150mm howitzer, a fast-firing 30mm MK 103 high-speed cannon was to be mounted by Rheinmetall.

3,7 cm FlaK 36 auf Sd.Kfz.6 (Sd.Kfz.6/2)
The chassis of an artillery tractor weighing 5 tons Sd.Kfz.6 was rebuilt into a self-propelled anti-aircraft cannon. The most mass-produced version of the BN 9 was used. A 3.7 cm Flak 36 was mounted.

3,7 cm FlaK 36/37/43 auf Sd.Kfz.7
Primarily, these anti-aircraft vehicles were to serve in Luftwaffe units, but of course they were also used by the Wehrmacht ground army.

44M Buzoganyveto
The anti-tank weapon was created because of the need of Hungarian troops to effectively fight against modern Soviet tanks. The Hungarians decided to go their own way and the Hungarian Military Science Institute (HTI) proposed the development of a powerful reactive projectile.

4TP

57mm anti-aircraft cannon R 10 on the chassis T-34/85
It was supposed to be a multi-purpose machine that could, in addition to anti-aircraft protection, be able to support the infantry in the fight against enemy infantry and light armored vehicles.
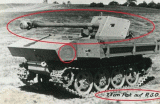
7,5 cm Pak 40/4 auf RSO

7,7 cm FK 96 L/23 auf W.D. Schlepper 50 PS
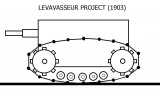
75 Levavasseur
In 1903, Capt. Léon René Levavasseur drafted the ideological concept of a self-propelled vehicle armed with a 75 mm cannon in a closed steel body with a crawler chassis. It was probably the first tank design in France.

8 cm Raketen Vielfachwerfer auf Fahrgestell Maultier
From the beginning of the war, the Waffen SS led the independent development of weapons from the army (Wehrmacht). One of them was an experimental version of the modified Soviet rocket launcher BM-8-48 known as "Katyusha". The captured rocket launchers were handed over to the protectorate companies Zbrojovka Brno and the Škoda plant. Vielfachwerfer was improved copy of the Soviet design of the launcher and the M-8 missile itself caliber 82 mm.

8 cm Raketen Vielfachwerfer auf Fahrgestell Maultier

8 cm rocket multi-purpose vehicle on vehicle Zgkw S303 (f)
Rocket launcher manufactured in Nazi Germany during World War II.

8,8 cm PaK 43 Ardelt

8,8 cm PaK 43 Ardelt-Krupp

8,8 cm PaK 43 Steyr
In 1944, the year of retreats and defensive battles of the German army, there was an acute need for mobile artillery armament in conventional infantry units. In retreat battles, the prevailing shortage of tractors resulted in high losses of conventional towed artillery weapons. Many were destroyed by their own troops only because of their immobility. Cannons such as 7.5 cm PaK 40, 8.8 cm PaK 43 or 10.5 cm PaFH 18 were too heavy for the soldiers and difficult to handle.

AH-IV-Hb
The last order of the Czechoslovak tankette of the AH-IV series was realized only a few years after the end of World War II. The customer was the African Ethiopian Empire (then called Abyssinia). Dancers were already an outdated concept before World War II, but due to the backwardness of this area, a tank design was sufficient for the Ethiopian army.

AMC 34

AMC 35

AMR 33

AMR 35 ZT 4
In the 1930s, French colonial units had considerably obsolete types of armored vehicles and tanks. The old Renaults FT were used, of the newer types there were Laffly 50 AM armored cars. Therefore, it was decided to modernize the armament of colonial troops. The choice fell on the type AMR 35.

AMX 38

Artillerie Panzer Beobachtungswagen (Sd.Kfz.251)

AT-1 (76.2 mm selfpropelled gun)
The AT-1 is perhaps the best known Assault Gun of the pre-war Red Army. This was a modified SU-1, with the KT-28 gun replaced by a PS-3 76.2 mm (3 in) gun. The vehicle was tested and it was found that the interior of the tank was insufficiently large. However, before the problems could be ironed out, the designer, P.N.Syachintova, was arrested and the project subsequently shelved.

Aufklärungspanzerwagen 38(t) (2 cm)(Sd.Kfz.140/1)

Australian Sentinel
In the early 1940s, Australia found itself in an unenviable position. Great Britain, the leading country of the British Commonwealth, faced Nazi attacks, its overseas colonies in Southeast Asia fell into Japanese hands one by one, and the imperial army approached the northern borders of Australia threateningly. The Japanese navy had ambitions to control both the Pacific and Indian Oceans, which would cause a complete blockade of the country. These facts led a country with almost no experience in the development of armored vehicles to the development of its own armored vehicles, represented by the Australian Cruiser Tank Mk.1 Sentinel.

Auto-Canon 75 mm Modéle 1913
A self-propelled version, on the back of a De Dion-Bouton truck chassis. The gun could be brought into action in five minutes, but its traverse and elevation were slow which combined with a lack of fire direction equipment limited its effectiveness. Puteaux completed 20 self-propelled versions in 1913 and by the end of WWI 196 had been completed.

Batignolles-Châtillon
In the 1930s, the French army issued an audition for a new light tank. It was to replace the obsolete Renault FT-17 tanks.

Batignolles-Châtillon DP 2
In 1935, the Compagnie Générale de Construction de Locomotives Batignolles-Chatillon presented a prototype of an amphibious tank built at the request of the Section Technique des Matériels Automobiles de Combat.
The first tests took place in March 1936 but the vehicle sank at the end of the demonstration.

Batignolles-Châtillon DP 3
Development successor of the Batignolles-Châtillon infantry amphibious reconnaissance tank from Nantes.

Bergepanther - draft horse of the Panzerwaffe

Bergepanzer 38(t)
After the introduction of the Jagdpanzer 38 (t) tank destroyers, there was a need for a light rescue vehicle, which was to serve to tow damaged or otherwise immobilized vehicles. Therefore, in the summer of 1944, BMM began working on such a machine, which was based on the design of Hetzer.

Bergepanzer 38 (t)
A light rescue tank, the history of which is closely connected with the Czechoslovak tank construction. The article also includes exclusive memories of the driver of this tank, who rode with him in 1959 in the post-war Czechoslovak army.

BM-13-16 Katyusha
The missiles were based on knowledge in the development of aircraft missiles RS-82 and RS-132. Launcher known as the prototype designations M-132, MU-2 and later serial designation BM-13-16, the best known and most used missile launcher of the USSR army. It consisted of 8 rails 5 meters long, two rockets each. Serial production began just before the invasion of the USSR.

Boirault No. 1
On August 24, 1914, Colonel Jean Baptiste Estienne formulated a vision of the all-terrain vehicles that would determine the direction of modern warfare, when he predicted a radical change. Immobile trench warfare was to be transformed by armoured vehicles equipped with weapons that were capable of moving in the terrain.

BOPAS
The project itself was probably created on the basis of a request from the Command of the Engineer Troops in 11/1954 was assigned the development of an armored personnel carrier called BOPAS (combat tracked vehicle).
BT-43
In 1943, an armoured personnel carrier project was developed in Finland using the platform of the captured Soviet BT-7 wheeled and tracked tank. A single prototype-demonstrator was produced.

Canon de 47 sur Vickers-Carden-Loyd T.13 B2
The B1 design was judged satisfactory enough to serve as a basis for the conversion of the remaining 23 gun tractors of the Chasseurs Ardennais. They were converted in 1936 on the same lines as the B1, with small differences of hull fittings, suspension, and internal compartmentation. As such, these B1 and B2s formed the bulk of the motorized regiments of the Chasseurs Ardennais, generally placed in 6-strong mobile units. One B2 of the cyclist frontier of Limburg, (Maaseik group) is still preserved at Brussels tank & army museum. However, the need of more motorized defense units and a more satisfactory design, as far of the crew protection was concerned, led to a redesign of the type.

Celere Sahariano

Char Amphibie Schneider-Laurent
The Char Amphibie Schneider-Laurent Tank was designed by M. Laurent and developed by Schneider, the tank was first seen in 1928. It had a boat shaped hull for amphibious operations and propelled in the water by a rear propeller. It operated on wheels whilst on the road and tracks off-road. Swapping between both systems could be completed by the crew from within the vehicle. Only one prototype was built.

Char B1 ter
The next development version of the B 1 ter arose from a 1935 request to increase the armour protection of the B 1 in the frontal parts up to 70 mm. ARL, FCM and Fives-Lille participated in the development and production, each company producing one prototype.

Char léger Renault transportable par avion
Like the British and Americans would do later in WWII with the Tetrarch and Locust tanks, the French also pursued the idea of an airborne tank. The French began playing with this idea in 1936, predating both the British and American tanks.

CTLS-4 TAC/TAY

Training mobile tank turret LT-38/37
When you think you're all over the best Czechoslovak light tank LT vz. 38, you come across a rare training aid from the post-war Czechoslovak army. "And then you roll your eyeballs."

Training mobile tank turret Sd.Kfz. 234/2
An extremely interesting use of the turret of the rare Sd. Kfz. 234/2 by the post-war Czechoslovak army.

CZK - T-50

E-100 Panzerkampfwagen Tiger-Maus
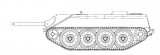
Entwicklungsfahrzeug E-10 Hetzer (project)
The E-10 was to be developed by KHD (Klöckner-Humboldt-Deutz AG) and the Magirus factory in Ulm and with the 7.5cm KwK L/48 as the main weapon. At KHD, however, the RSO/03 was in production at the time and enjoyed higher priority. One of the special features of the E-10 was certainly the lowerable undercarriage, thanks to which the overall height of the vehicle silhouette could have been reduced by almost 40cm. However, with the availability of the first prototypes of the Jagdpanzer 38 D, the E-10 was taken out of the planning and was already obsolete.

FCM 1A
In 1916, the French army launched a competition to develop heavy tanks. In contrast to the classic English turretless concept, the French concept envisaged a modern concept of a single-track tank.

FCM 2C

FCM F1

Feuerlilie 25/55

Flakpanzer IV
In a report from 3.1.1944 on a consultation with Albert Speer with representatives of the military, there was a proposal to use an anti-aircraft system with a pair of 3 cm cannons designed for submarine armament on the platform of a medium tank Pz.Kpfw.IV (U-Bootturm mit 3 cm Zwilling auf Pz. IV).

Flakpanzer IV Ostwind
Simultaneously with the development of the Wirbelwind anti-aircraft tank, there was also the development of a self-propelled anti-aircraft tank armed with a 37 mm cannon, which was given the combat name Ostwind (Eastern Wind). The chassis of the medium tank Pz.Kpfw.IV ausf.J.

Flammpanzer 38(t)
On November 27, 1944, on the orders of Adolf Hitler himself, a certain number of flame-thrower tanks were ordered for the planned operations. At that time, the successful Jagdpanzer 38(t) tank fighter was also available, and it was decided that 20 flame-throwers would be created on its basis. The machines were taken from the production factory and sent for rebuilding on 8.12.1944. A Köbe flamethrower was fitted instead of the gun.

G1 P
The final medium tank programme, later referred to as the "G1", was preceded by a long period of differing Army requirements. Despite a wealth of tank development and production in the 1930s, the French Army lacked a quality medium tank.

Grosstraktor Daimler-Benz

IS-100
This machine was to be the first successor of the heavy tank IS-1, whose 85mm cannon was not a completely adequate response to the new German tanks.

ISU (BTH 803) civilian conversion to tracked bulldozer
Just a small suggestion and you remember one inconspicuous photo in an aviation magazine. And for the next almost 20 years there will be a quantum of photos, information and surviving vehicles that hardly anybody remembers. Isn't this research wonderfully exciting?

Jagdpanther

Jagdpanther Ausf.G1/Ausf.G2
Jagdpanzer 38(t)

Jagdpanzer 38(t) Starr
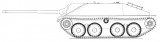
Jagdpanzer 38D
The small and cheap Jagdpanzer 38(t) proved to be an effective tank destroyer. The main problem with it was that BMM and Škoda who made the vehicles simply could not keep up with the demand. In the hope of getting its production repositioned to Germany in late 1944, Alktett was instructed to oversee the projected construction of a new vehicle, later designated as Jagdpanzer 38 D. While the work continued until the end of the war, only two prototypes were completed (or none at all).

Jagdpanzer IV L/48

Kätzchen 38t
Despite the support of the Heeres Waffenamt and WaPrüf 6 of the Auto Union armored personnel carrier project known under the code name Kätzchen, there was an effort to use the Pz.Kpfw.38 (t) tank chassis and B.M.M.

Kätzchen K1

Kätzchen K2
The first mention of the nickname "Kätzchen" was found in the report of the General Staff of 15.2.1943. There was an effort to speed up the production of Kätzchen, the conversion of production from Sd.Kfz.250 and Sd.Kfz.251 was to be completed by the end of 1943. Gradually, the production of half-track transporters was to be reduced and in the summer of 1944 was to be fully stopped.

kleiner Panzerbefehlswagen (Sd.Kfz.265)
KOBO-3

Kugelblitz - the best flakpanzer?
The last of the last. Ball lightning - the latest German anti-aircraft tank, which did not manage to show its advantages.

L.K.A.1

L.K.A.1

Lancia 1Z (1ZM)
The Lancia 1Z and the Lancia 1ZM were two variations of an Italian armoured car built during World War I and which saw limited service during that war, the interwar period, and during World War II.

leichte Selbstfahrkanone (L.S.K.)

leichter Zugkraftwagen 3 t (Sd.Kfz.11)
The Sd.Kfz. 11 was a German half-track vehicle developed as an artillery tractor from 1934 and used by the Wehrmacht on all fronts during the Second World War. It belongs to the group of special-purpose vehicles. About 8800 units were built until 1944.

Leichttraktor Krupp

Leichttraktor Rheinmetall-Borsig

LK II

Lorraine 38L
France's unconventional solution to transporting troops into battle. The result is a conversion of the Lorraine 37 artillery tractor, adding a protection to the open load area and towing an armoured trailer for the additional men of the "Chasseur Portes" squad.

LP-157
After the failure of the project to fit the 57 mm R 10 anti-aircraft gun to the T-34/85, efforts continued to develop it further. In 1955, a new design for a similar gun and platform combination was requested by the Army.

LT-40

Marienwagen II
A modified truck in which conventional wheel axles have been replaced by tracked chassis.

Max and Moritz, insurmountable brothers
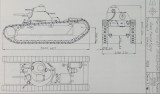
Mogårdshammar A
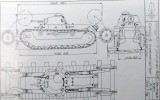
Mogardshammar B

MP 3008 (Gerät Neumünster)
The fate of this weapon is more than just closely linked to the English submachine gun Sten. Soon after the start of its production, a number of specimens fell into the hands of the Germans. They were seized from supplies to the French resistance and later after the landing attempt at Dieppe. When the Walls fell into the hands of German army experts, they were literally shocked by his primitive appearance and their test results were clearly negative.

Mystifications, mistakes and facts about German technology

NAHUEL D.L.43

Neubaufahrzeug Ausf. B
The German Neubaufahrzeug tank was the first prototype heavy tank for the Wehrmacht after Adolf Hitler took power. This heavy and slow multi-tower tank could hardly be used for Blitzkrieg tactics and therefore only 5 units were produced. These machines were mainly used for promotional purposes, but took part in the fighting in Norway in 1940.

Type 2 Ka-Mi Amphibious Tank
The design of the new Mitsubishi amphibious tank was created at the request of the Japanese Imperial Navy in 1940. The machine was intended to act as a support in the landing operations of the Japanese Special Naval Landing Forces.
Armored car S-971 Jarmila

P-II-a

P-II-b
In 1/1935, VTLÚ was given technical specifications for the development of a new attack tank to support infantry units. The submitted proposals for the tank led to January 13, 1936 to order a prototype made of unarmored steel.

Panther II - alternate in offside

Panzer IV/70 (A)

Panzer IV/70 (V)

Panzerbefehlswagen III Ausf.K
The absence of cannon armament in the command tanks Panzerbefehlspanzer III Ausf.D1 / Ausf.E / Ausf.H caused that in direct contact with enemy tanks could not effectively fight and this was the cause of subsequent losses of these tanks.

Panzerbefehlswagen IV Ausf.H/J
Command modifications were created on the platforms of the refurbished PzKpfw.IV Ausf.H. The machines differed from standard tanks externally by only two antennas. By placing another radio station in the tank, the supply of ammunition for the cannon had to be reduced.

Panzerbeobachtungswagen V
At the end of 1942, a project of a reconnaissance artillery-guidance version of the PzKpfw.V "Panther" tank was created. Originally, the cannon was Kw.K. 42 L / 70 replaced by a 50 mm cannon Kw.K. 39/1. Additional armament was to form a machine gun MG 34. The original plan to arm the tank with a cannon was later reconsidered and it was decided to replace the cannon armament with a dummy one.

Panzerwerfer 42 auf Maultier
The Panzerwerfer 42 auf Maultier was used for larger scale rocket barrages against Soviet positions where a large bombardment of a big area would be more effective than more accurate artillery fire. The Panzerwerfer's rocket barrages covered much larger areas and added more psychological elements to the fight: the amount of noise, smoke, splinters, and flying debris as the rockets hit and exploded was considerable. The extensive use on the Eastern Front showed that this weapon could be employed effectively on the Western Front as well.

Flamethrower tank PM-1

PPG
The project of a Soviet machine gun tank from the beginning of World War II.

Prague DT-III (DTH-III)
After the end of World War II, the concept and components of the chassis of the Jagdpanzer 38 (t) tank fighter were used for the construction of artillery tractors from the Prague CKD (ex. BMM), which began the development of tractors of three weight categories.

Praga MT
Projection design of the Praga tank from 10.2.1927. The project number was 6821 and the project appeared under the name Armored tank Praga MT (MT = small tank).
Praga T-6
The most numerous and most exported version of the artillery tractor by ČKD (Praga). A number of exotic customers, there is a lot of previously unknown information in the subject.

Praga V3S-O-1

Articulated tank project
A truly curious design by Delahay's chief designer from 1937.
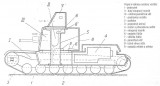
Tank project with a rotating tower and a fixed extension

PT-1

Pz.Kpfw. 38 (t) neuer Art

Pz.Kpfw. I Ausf. F

Pz.Kpfw. I Ausf. F - a heavy cry in the dark

Pz.Kpfw. II Ausf. G

Pz.Kpfw. II Ausf. J

Pz.Kpfw. II Ausf. L

Pz.Kpfw. III Ausf. D
The Panzer III Ausf.D was the last version of the experimental series developed starting from the Ausf.A. It incorporated a number of improvements, of which the most obvious was the redesign of the rear engine compartment and introduction of a slightly modified 8-wheel suspension. It was also different from the previous version by being built in somewhat larger (but still limited) numbers. The Panzer III Ausf.D also had the longest service life, soldiering on to 1941 and possibly even after that.

Pz.Kpfw. IV Ausf. G with a hydrostatic drive

Pz.Kpfw. IV Ausf. H
Production of the Ausf.H began in late 1942, and many innovations were implemented that significantly increased the combat value of the vehicle. The most significant innovation was the replacement of the main gun. The tank received a new KwK 40 L/48 gun with an extended barrel to 48 calibre (the previous G version had a KwK 40 L/43 gun with a barrel length of 43 calibre). The new gun achieved a higher muzzle velocity, and the gun was able to penetrate thicker armour-piercing obstacles with anti-tank ammunition than the previous gun with a shorter barrel.

Pz.Kpfw. IV Ausf. J
The Panzerkampfwagen IV (Pz.Kpfw. IV), commonly known as the Panzer IV, is a German medium tank developed in the late 1930s and used extensively during the Second World War. Its ordnance inventory designation was Sd.Kfz. 161.
The Panzer IV was the most numerous German tank and the second-most numerous German fully tracked armoured fighting vehicle of the Second World War; 8,553 Panzer IVs of all versions were built during World War II, only exceeded by the StuG III assault gun with 10,086 vehicles.
Pz.Kpfw. IV Ausf. J (10./B.W.) is the last version, which was created in the critical situation of the German industry and bore the signs of saving time and material needed to produce the tank.

Pz.Kpfw. V Ausf. A Panther

Pz.Kpfw. V Ausf. D Panther

Pz.Kpfw. V Ausf. G Panther
Pz.Kpfw. V Panther - in the service of foreign armies

Pz.Kpfw. VI Ausf. B Tiger
The origins of the creation of the Tiger II go back to the times when the first prototype of the Tiger I(P) was not built yet. The history of the VK 45.01(P) (Porsche's project for a new heavy tank Tiger) is known. Porsche was hoping for with a win in the competition for a new heavy tank, and therefore started production of the first 100 platforms. After the lose of most of the platforms will serve for conversion to a fighter tank destroyer Ferdinand/Elefant. Porsche's plans, however, reached even further.

Pz.Kpfw. VI Ausf. E Tiger

Pz.Kpfw. VII Löwe

Pz.Kpfw.-Turm 35 (t) (Normalserie)
Towers from decommissioned tanks Pz.Kpfw.35 (t) (ex. LT vz.35) and converted Mörserzugmittel 35 (t) were used as permanent firing posts. The designation "Normalserie", which should denote the towers from the standard mass production of tanks in this case is incorrect (but it is official). The tower was modified.

PzKpfw VI Tiger II

R 11 (100 mm anti-aircraft gun)
When a top Czechoslovak design ends up in a drawer.

Räder-Ketten-Schlepper mit Wechsellaufwerk

Renault 35 in the Bulgarian army
The contract for the purchase of 40 French Renault 35 light tanks between the Bulgarian Army and the German company AGK, Berlin was signed on 23.4.1941. The Bulgarians paid 2,377,280 Reichsmarks for the goods.

Char D3
In the early 1930s, when Char D had not entered production, Renault was ordered to develop an improved version and a colonial version of Char D. Eventually, the improved version developed into Char D2, and the colonial version developed into Char D3, which has never entered production.

Renault FP
In 1915, a request arose from the French army for the development and construction of a tracked vehicle, which was to serve as a carrier of cannon armament. Artillery mechanization was required, which had certain advantages over pulling parts. Towed cannons can sink or be damaged by dragging. However, the size of the weapons carried was limited to field weapons and light howitzers, because a vehicle for transporting heavy artillery would be large and cumbersome.

Renault FT in the Czechoslovak Army
The first requirement for the purchase of these tanks is a telegram of the commander of the eastern group of Czechoslovak troops, French General Hennocque, dated July 3, 1919 in connection with the fighting against the Hungarian Bolshevik troops.

Renault NC 1

Renault NC 2
Derivative of the legendary French tank Renault FT 17 from 1925. The new tank arose from the need to modernize its predecessor, with the proviso that the tank was to be fully autonomous for longer moves without the need for tank transporters.

Renault R 40

Renault R-35 (2 pdr gun)
Several, originally French, Renault R 35 tanks that found themselves in the arsenal of the Syrian army were rearmed with the British 2-pounder gun.
Renault UE
In 1930 the Commission de Vincennes decided to develop a light armoured vehicle able to tow and supply small cannon and mortars. In 1931 the Renault company was given the contract for production of its Renault UE, combined with the Renault UK trailer. In 1937, from a number of competitors, the Renault UE2 was chosen as an improved type for large-scale production. Of both types combined over five thousand were built, including licence production in Romania, and they were part of the standard equipment of all French infantry divisions. Most Renault UE vehicles in French service were unarmed; those in 1940 captured by Germany were used for a variety of purposes, including being armed with machine-guns, antitank-guns and rocket artillery.

Renault YS 2
The Renault YS 2 was an artillery observation vehicle with advanced telemetric optics, including a rangefinder turret. On 20 July 1936 it was decided by the Artillery to acquire such a type, called the voiture blindée tous terrains d'observation d'artillerie.

Résistance Léger Char Lorraine 37L
There was probably no official naming of the conversions covered by this topic. These were conversions of Lorraine 37L artillery tractors to light tanks, which came about after the annexation of unoccupied parts of France by German troops.

Resita cal.75 TA Md.1943

Rheintochter

T-34 platform cable groover and installer
The top civilian conversion of the famous T-34 tank, which combined a grooving vehicle and a cable-laying vehicle. Unlike the use of lighter military platform types that could only handle one task, this platform was sufficiently sized to handle both functions.

S.U. (Škoda Š-II)
The SU project (S.Ú.V. - medium attack car) of the Škoda Plzeň company was created in 1933 as a reaction to the competing P-II (LT vz.34) of the ČKD company. The prototype was built in the first half of 1934 and according to the new categorization of tanks received the designation Š-II.

Saint-Chamond model 1921
The project of the Saint-Chamond wheeled and tracked tank from 1920/21. At that time, the idea of combining two types of chassis - tracked and wheeled - into one hybrid type was more or less experimentally promoted.

Self-propelled gun SU-76M
A short history of the emergence of a modernised version of a light self-propelled cannon.

SAu 40 (CAM 2)

Saurer RK-9

Schneider CA 2
Shortly before the arrival of the first French tanks in the active army, the most prescient tank theorist (and also a practitioner), General Etienne, suggested to the commander-in-chief of the ground forces that a command tank be created.
"I believe that assault artillery units have to manoeuvre on the battlefield, so it is necessary to provide tanks for their command with the following characteristics: a ground speed of 10 km/h, crossing trenches 1 metre wide, a crew of 4 men, armed with one or two machine guns and a 37mm gun that could fire forward and sideways. The armour would be reinforced to 15 mm. It makes sense to provide for the construction of 50 command tanks."
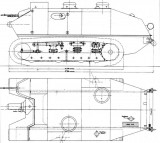
Schneider CA 3 (project)
The CA3 tank, developed on the basis of the CA1 tank, was produced in several variants, all of which were rejected by General Estienne.
Despite the increase in weight, the motorization did not improve, and the general rightly believed that by the time of the expected 1918 deployment, this machine would be completely outclassed.
Paradoxically, the turret model was strongly opposed, but this must be seen in the context of a time when the threat of enemy tanks did not exist. Only forts, machine gun nests or artillery batteries could be potential targets, so installation in a casemate was quite sufficient.

Schneider-Renault typ A
The project, which was created at the request of the French Army to develop and introduce a new tank for infantry support with the ability to fight against other tanks.

schwere Wehrmachtschlepper - unsuccessful post-war evolution
Where others end, others ... end as well. Unsuccessful post-war Czechoslovak evolution of the German artillery tractor sWS. Another in a series of extremely interesting projects combining German and Czechoslovak potential.

Sd.Kfz. 250/9

Sd.Kfz. 7/1
These anti-aircraft vehicles were developed and manufactured primarily for Luftwaffe units, later used in the Wehrmacht, where they served as anti-aircraft protection armored units armed with tanks, tank destroyers and self-propelled guns.

Sd.Kfz.10/2 (decontamination vehicle)
This decontamination vehicle Sd.Kfz.10 / 2 had a storage platform with steel profile sides created behind the driver's and passenger's cab. Eight barrels of decontamination chemical were carried on the storage area.

Sd.Kfz.10/3 (poison gas sprayer vehicle)
Sd.Kfz.10 / 3 was a vehicle designed to create infestation using liquid warfare agents. A steel tank for 500 liters of toxic substance was mounted in the rear of the vehicle. Using a compressor and a distribution system terminated by swinging nozzles, the 16-meter-wide section was contaminated.

Sd.Kfz.11 Raketenwagen
Special version of the half-track tractor category 3 tons Sd.Kfz.11 designed for coastal rescue units (Deutsche Gesellschaft zur Rettung Schiffbrüchiger - German Naval Search and Rescue Service). It was a rescue system in such a way that a rescue rope was transported to the rescued person or ship with the help of rockets.

schwerer Nebelwerferkraftwagen (Sd.Kfz. 11/5)
German half-track that saw widespread use in World War II. Its main role was as a prime mover for medium towed guns ranging from the 3.7 cm FlaK 43 anti-aircraft gun up to the 10.5 cm leFH 18 field howitzer. It could carry eight troops in addition to towing a gun or trailer.

Sd.Kfz.221

Sd.Kfz.231 (8-rad)
In the first half of the 30s of the 20th century, it was decided to develop a replacement for heavy armored cars Sd.Kfz.231 (6-rad). A modern armored vehicle on an 8-wheel chassis was to be created, which was to form the armament of reconnaissance units, mainly in tank divisions.

Sd.Kfz.250/1

Sd.Kfz.251 (OPp 3t N) in the Czechoslovak army

Sd.Kfz.251/10

Sd.Kfz.251/20 (infra)

Sd.Kfz.251/22

Sd.Kfz.254
After the annexation of Austria by the German empire the austrian wheel-tracked artillery truck Saurer Räder-Raupen RR-7 caught the eye of the German command.

Sd.Kfz.9/2 (heavy tractor with 10 t crane)
One of the versions of the mobile crane on the SdKfz.9 platform. A Demag crane with a capacity of 10 tons is mounted on the loading area of the machine.

Semovente L 40 da 47/32

Semovente M 41M da 90/53

Sisu
In 1936, the Finnish Ministry of the Interior decided to commission the development and production of a new armored vehicle for police forces.

Škoda ČKD ŠP-IIb
The failures of Škoda (Š-II-b) and ČKD (P-II-b) in the development of a new infantry tank led to their cooperation on a joint project.

Skoda RSO (Porsche Typ 175)
In the years 1941/42, a tractor for the eastern front was developed. Ferdinand Porsche signed this type of design and the Škoda company was entrusted with the production. The prototype was built at the end of 1942 and serial production took place in 1943. Originally, the order sounded to 200 pieces, later it was reduced to 100 pieces.

Škoda Š-I-D
The T-32 (Š-I-D) tankette was a Czechoslovak-designed tankette used exclusively by the Kingdom of Yugoslavia during World War II. Its design was based on the Škoda MU-4 tank and built specific to Yugoslav specifications.

Škoda Š-I-P (T-2)
At the request of an Afghan customer, in 1938 the Škoda company developed a towerless tank project called Š-I-P.

Škoda Š-I-SPO
In 1937, the Škoda company built a prototype of a tank with a rotating tower, which, according to plans, was to form the armament of mixed reconnaissance divisions of rapid divisions.

Skoda Sh-IIc

Škoda T-11
This is a new factory designation introduced in 5/1939, which replaced the original designation of the tank Š-II-a adopted by the Czechoslovak army as LT vz.35. The light tank project was the result of an order from the army of the Kingdom of Afghanistan.

Škoda T-15

Škoda-Praga L
One of the first armored car designs in the newly founded Czechoslovakia from 1921. The Škoda design used the platform of the Praga L 7.series truck, whose designation was adopted by this armored car. A square armoured body made of thin armoured plates was mounted on the platform. A swivel turret was mounted on the roof of the vehicle, in which a 37 mm gun and a heavy machine gun were mounted.

Somua S 35
The SOMUA S35 was a French cavalry tank of the Second World War. Built from 1936 until 1940 to equip the armoured divisions of the Cavalry, it was for its time a relatively agile medium-weight tank, superior in armour and armament to its French and foreign competitors, such as the contemporary versions of the German Panzer III medium tank. It was constructed from well-sloped, mainly cast, armour sections, that however made it expensive to produce and time-consuming to maintain.

ST-I - Use of ex.Jagdpanzer 38 (t) in post-war czechoslovak army

STA Fouché No.1 Type A, Type B, Type C
In cooperation with Service Technique Automobile (STA) and Lieutenant Fouché, prototypes of the first French tanks were created.
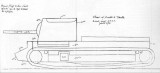
STCC
In 1928 started a French general Etienne development program for a special type of vehicle called a "defensive role of the tank" (char darrêt), which should have a weight of from 45 to 55 tonnes. The main idea was to create a heavily armored and armed vehicle, which should strengthen the Maginot line as the mobile protection against enemy armored technique.

Strv fm/31
Strv m/31

StuG III Ausf.G

Sturmgeschütz IV für 15 cm Sturmhaubitze 43
The effort to acquire an assault self-propelled gun dates back to the first battles of World War II. The first attempt was the 15 cm S.I.G.33 Sfl. auf Pz.Kpfw. I ohne Aufbau Ausf.B, followed by 15 cm s.I.G. 33 auf Fahrgestell Pz. Kpfw. II (Sf). After these self-propelled guns of open design, the Sturminfanteriegeschütz 33 self-propelled gun was developed, which featured a fully enclosed fighting compartment that perfectly protected the crew from small arms fire and artillery shell splinters.

Sturmgewehr 45 (Mauser)
The StG 45(M) (abbreviation of Sturmgewehr 45, "Assault Rifle 45") sometimes referred to as the MP 45(M), was a prototype assault rifle developed by Mauser for the Wehrmacht at the end of World War II, using an innovative roller-delayed blowback operating system. It fired the 7.92×33mm Kurz (or "Pistolenpatrone 7.9mm") intermediate cartridge at a cyclic rate of around 450 rounds per minute.

Sturmpanzer Ausf.I-IV

SU-76
The anabase of the origin of this self-propelled gun was long and interesting. This light self-propelled gun was the first mass-produced machine of this category in the USSR. It was created in response to German self-propelled guns, which showed great benefits.

sWS - the last heavy tractor of the Wehrmacht
schwerer Wehrmachtschlepper was the last attempt to create a powerful heavy tractor. A unified emergency for little money, which also survived its "death" in evolutionary form in post-war Czechoslovakia.
T-100

T-150
It is a modified KV-1 with a 76mm F-32 cannon. It had an enlarged thick frontal armor to 90mm, modifications to the turret and a few other minor modifications.

T-23
The T-23 tank was based on a lightweight towerless version of the T-18 tank design. The development of the T-23 tank took place simultaneously with the development of similar T-17, T-21, T-22 tanks in the period 1929/30.

T-55 slag disruptor
Unneeded tank chassis become a profitable commodity in the civilian economy after service in the army. One of the conversions is this modification of the military repair plant VOP 025 Nový Jičín, where the unneeded chassis of the T-55 tank was adapted for breaking up hot slag under the blast furnace.

TACAM R-2
The TACAM R-2 was a Romanian tank destroyer used during World War II. It was built by removing the turret of the R-2 light tank (Panzer 35(t)) and building a pedestal to mount a Soviet 76.2 mm (3.00 in) ZiS-3 field gun in its place. A three-sided fighting compartment was built to protect the gun and its crew. Twenty were built in 1944, but only one is known to exist today. It participated in the Budapest Offensive and the Prague Offensive.

TACAM T-60
How to produce a tank fighter when we don't have enough industrial capacity? We will use the adversary's technology! The Romanian way to meet the needs of the army.
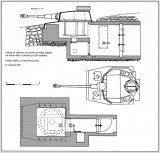
Tank tower T-40/75 N on a reinforced concrete base
In 1954, the idea arose to use the towers of the captured German medium tanks Pz.Kpfw.IV as permanent fortress palposts in the border zones of the Czechoslovak Republic. The tank cannon itself was still evaluated as effective in this period and the army had a sufficient supply of ammunition for the cannons.

Tiger II - A worthy successor or a costly mistake?

TKS

Dicker Max
A difficult road to failure. A strong man who failed. That's how you could call the development of a heavy self-propelled gun designed for the planned destruction of fortresses, and which made its mark on the Soviet plains as a heavy tank destroyer.

V-8-H

Versuchflakwagen
At the beginning of the project of a heavy self-propelled anti-aircraft tank was the order of the German army for three 8.8 cm self-propelled guns Flak L / 56 mounted on the platform Pz.Sfl.IVc developed by Krupp. These were to serve to destroy the heavy fortifications of the Maginot Line during the planned invasion of France. The construction of these machines was not in time to participate in occupation of France and subsequently their role was reclassified as tank destroyers. However, due to their light armor, this was not an appropriate task. They would be easy prey when clashing with enemy tanks.

Versuchflakwagen Leichte

VK 20.01 (D)

VK 20.01 (D) - the first German tank with a diesel engine

VK 28.01 Mehrzweckfahrzeug
That the VK 28.01 "Mehrzweckfahrzeug" standardised platform project is little known? What about its planned version for moving on rails?

VK 30.01 (D)

VK 30.01 (D) - Panther from the competition

VK 30.01 (H)

VK 30.01 (P) Leopard

VK 36.01

VK 36.01 unsuccessful journey to the Tiger tank

VK 45.01 (P)

Wasserfall

Z.W.40

„Rikstanken“ Norge
Badges
| News Category |















|
| Personalities Category |















|
| Units Category |















|
| Armoured Vehicles Category |















|
| Artillery & Rockets Category |















|
| Soft Skin Vehicles Category |















|
| Land-Based Air Defence Category |















|
| Armament, Weapon Systems, Equipment and Accessories Category |















|
| Airplanes Category |















|
| Helicopters Category |















|
| Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Category |















|
| Vessels Category |















|
| Submarines Category |















|
| Communication Systems Category |












|
| Small Arms Category |















|
| Dress & Mess, Uniforms & Accoutrements Category |















|
| Weapons of Mass Destruction Category |















|
| Space Technology Category |















|
| Medals & Decorations Category |















|
| Geographic Information Category |















|
| Crimes Against Humanity Category |















|
| Terrorism & Piracy Category |















|
| World Religions Category |















|
| Explanatory Dictionary of Military Terms Category |















|
| Annotations and Book Reviews Category |















|
| Books & Movies Category |















|
Medals and awards

|
Rytířský kříž www.valka.cz |

|
Důstojnický kříž www.valka.cz |

|
Železný kříž www.valka.cz |

|
Kříž www.valka.cz |

& bar (10) |
Řád 17. května & Bar |

|
Řád 17. května |

|
Řád redakce www.valka.cz se zlatou stužkou |

|
Řád redakce www.valka.cz se stříbrnou stužkou |

|
Řád redakce www.valka.cz |

& bar (5) |
Medaile Cti k titulu Hrdina serveru www.valka.cz |

|
Hrdina serveru www.valka.cz |

|
Zlatá hvězda www.valka.cz |

|
Stříbrná hvězda www.valka.cz |

|
Bronzová hvězda www.valka.cz |

& bar (18) |
Velký kříž čestné legie serveru www.valka.cz |

|
Komander čestné legie serveru www.valka.cz |

|
Důstojník čestné legie serveru www.valka.cz |

|
Rytíř čestné legie serveru www.valka.cz |

|
Čestná legie serveru www.valka.cz |

|
Řád slávy www.valka.cz s diamantovou stužkou |

|
Řád slávy www.valka.cz se zlatou stužkou |

|
Řád slávy www.valka.cz se stříbrnou stužkou |

|
Řád slávy www.valka.cz |

& bar (5) |
Kříž za zásluhy o forum 1. třídy |

|
Kříž za zásluhy o forum 2. třídy |

|
Kříž za zásluhy o forum 3. třídy |

|
Medaile za zásluhy o forum 1. stupně |

|
Medaile za zásluhy o forum 2. stupně |

|
Kříž za zásluhy - Zbraně a vybavení - Pozemní technika |

& bar (29) |
Medaile za příspěvky ke Zbraním a vybavení - Pozemní technika |

|
Krzyż Walecznych |

|
Pour le Mérite |

|
Eichenlaub und Schwertern zum RK des EK |

|
Ritterkreuz des Eisernes Kreuzes |

& bar (3) |
Ehrenblatt Spange des Deutschen Heeres |

|
Bayerische Tapferkeitsmedaille |

|
Ehrenkreuz |

& bar (1) |
Kriegsverdienstmedaille |

|
Spange 1939 zum Eisernes Kreuz 1.Klasse |

|
Spange 1939 zum Eisernes Kreuz 2.Klasse |

|
Eisernes Kreuz 2.Klasse (1914) |

|
Eisernes Kreuz 1.Klasse (1914) |

|
Kjókudžicušó |

|
Pamětní mince |

|
Croix de Guerre 1939-1945 |

|
Croix de la Valeur Militaire |
Join us
We believe that there are people with different interests and experiences who could contribute their knowledge and ideas. If you love military history and have experience in historical research, writing articles, editing text, moderating, creating images, graphics or videos, or simply have a desire to contribute to our unique system, you can join us and help us create content that will be interesting and beneficial to other readers.
Find out more















